How to Add External Users to Microsoft 365 for Collaboration

If you are using Microsoft Teams and would like to be able to communicate with the external users, there are certain steps that you need to take before they can join your Teams. For example, you can add a user from Contoso.com join your Microsoft Teams. You can also add users that don’t belong to any organization and are using free web-based emails, such as Gmail or Outlook.com, so they can be added to your Microsoft Teams channels and collaborate with you just like any other employee within your organization. As far as Microsoft 365 is concerned, external users are people that are not part of your organization.
Before you consider adding an external user to your organization, it’s helpful to understand the difference between External access and Guest access. I will explain these two in the next section. The second important thing is to read my article Understand the Impact of Enabling Guest Access in Microsoft Teams. There are some consequences of enabling Guest access in Teams, which I have discussed in my article in detail.
Microsoft offers two options for communicating with external users: External access and Guess access. They both are meant to give access to people who are not part of your organization, but there is a distinction to how they are treated by Microsoft Office 365.
External access
Microsoft defines External access as “a way for Teams users from an entire external domain to find, call, chat, and set up meetings with you in Teams.” For example, with external access anyone in the world who is using Microsoft Teams can use your email to find and contact you. However, External access alone doesn’t allow users to be added to your Microsoft Teams. The external user will need Guest access to join Microsoft Teams and collaborate with your employees.
Guest access
A Guest access refers to giving access to your Microsoft 365 tenant to an external user, such as a consultant, partner, or vendor. A guest doesn’t need to be a business user who has a Microsoft 365 account in Azure Active Directory (AD) at another organization. People who use a free email account (Gmail, Outlook.com, etc.) can also join Microsoft Teams. For the most part Guests are treated just like a Teams user in your own organization because their account is added to the Azure AD. However, there are some differences between the two and Microsoft has published a comparison of team member and guest capabilities.
The Guest access allows external users to access resources like teams, documents in channels, chats, applications, and Teams meetings on your organization’s Microsoft 365 tenant. You can add a user as Guest in Azure AD at https://portal.office.com/adminportal/home?#/GuestUsers. You will need administrative level permissions to access Azure AD, such as Global Admin. If a guest user is signed into her company’s Microsoft 365 portal, she would have to sign out and then use her guest account to sign in to your organization’s Microsoft Teams.
Microsoft has posted the following comparison of External access vs. Guest access. Use these tables only as a reference and visit Microsoft’s website for the latest information.
| Your Company’s Users Can Do This: | ||
|---|---|---|
| Users can | External access users | Guests |
| Chat with someone in another organization | Yes | Yes |
| Call someone in another organization | Yes | Yes |
| See if someone from another organization is available for call or chat | Yes | Yes |
| Search for people in other organizations | Yes | No |
| Share files | No | Yes |
| See the out-of-office message of someone in another organization | No | Yes |
| Block someone in another organization | No | Yes |
| Use @mentions | Yes | Yes |
External Users Can Do This:
| External Users Can Do This: | ||
|---|---|---|
| People outside your organization can | External access users | Guests |
| Access Teams resources | No | Yes |
| Be added to a group chat | No | Yes |
| Be invited to a meeting | Yes | Yes |
| Make private calls | Yes | Yes |
| View the phone number for dial-in meeting participants | No | Yes |
| Use IP video | Yes | Yes |
| Use screen sharing | Yes | Yes |
| Use meet now | No | Yes |
| Edit sent messages | Yes | Yes |
| Delete sent messages | Yes | Yes |
| Use Giphy in conversation | Yes | Yes |
| Use memes in conversation | Yes | Yes |
| Use stickers in conversation | Yes | Yes |
| Presence is displayed | Yes | Yes |
| Use @mentions | Yes | Yes |
Just to avoid any confusion, let’s summarize the terminology.
- External user: A person that’s not not part of your organization. Whether people are given External access or Guest access to your organization, they are all considered external users.
- External access: A method used by Teams users of one organization to communicate with Teams users of another organization anywhere in the world.
- Guest access: Gives access to your Microsoft 365 tenant to an external user, such as a consultant, partner, or vendor. Guest access can be used to collaborate with external users in Teams, SharePoint, OneDrive, etc.
Fasten Your Seat Belt and Get Ready…
Now that you understand the concept of External access and Guest access, I will take you on a tour of all the places where you need to configure access for the external user. Depending on why you need to configure these settings and what your goal is, you will enable features accordingly. As a best practice, always document the changes you make to your configuration and add explanatory notes so you can use the documentation as a reference in the future.
| Your Tenant Security is Paramount: Although it’s possible to allow external users access to Microsoft Teams and the rest of your Microsoft 365 tenant without risking your security and privacy, some organizations don’t follow all the security best practices to properly secure their Microsoft 365 tenant. This makes them vulnerable to cybersecurity attacks. If you’re not 100% sure what you’re doing when configuring Microsoft 365 services, it’s best to hire a Microsoft 365 certified professional to assist you. |
Configuring External Collaboration Settings in Azure AD
The settings in Azure AD overwrite all other places, so this is the place where you want to start and make sure Guest access is enabled (assuming your organization policy allows Guest access).
WARNING! If you didn’t read my article I mentioned at the beginning, now will be a good time to read it before proceeding.
To configure External access, sign in to Microsoft 365 as a Global Admin and go to External collaboration settings in the Azure AD portal. Only trained professionals certified to modify Azure AD security should be configuring Azure AD security. Below is an example of a secure external collaboration configuration. Adjust these settings as necessary. For example, change the Guest invite settings for your organizations to lower the security by selecting the first or the second radio button.
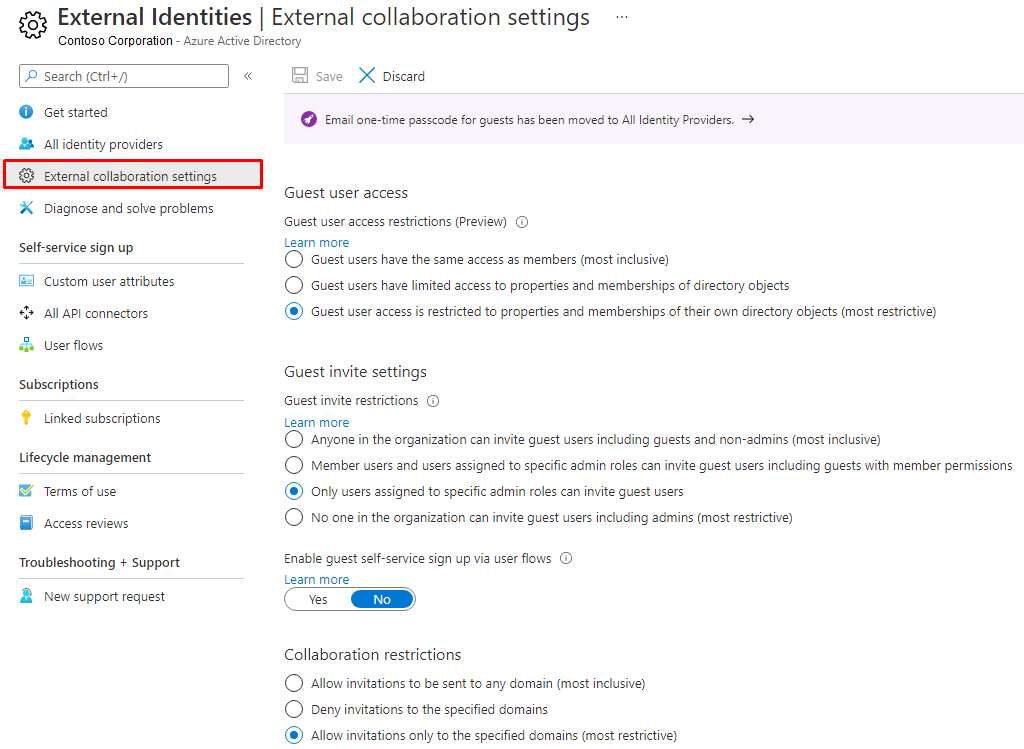
Configuring External Access for Teams
Once Azure AD has been configured to allow Guest access, you also need to allow external users access to your Teams. Go to the Teams admin center -> Org-wide settings -> External access. By default, your organization can communicate with all external domains. However, you can allow certain domains and disallow others. By default, External access is enabled for all domains in Microsoft Teams.
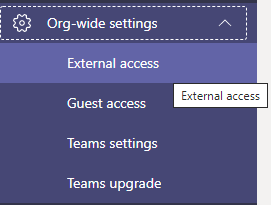
Enable the External access for Teams users, if it isn’t already enabled.
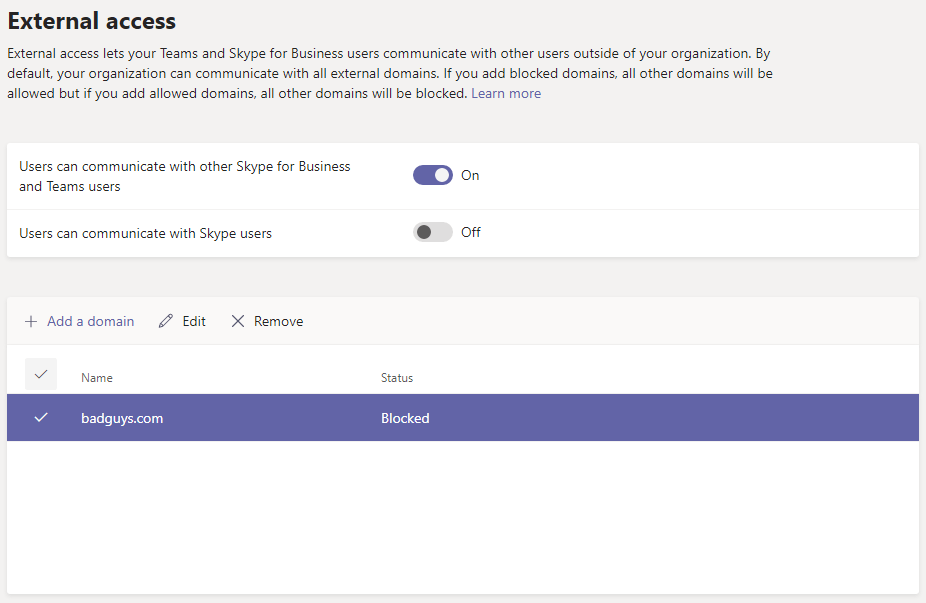
For security reasons, External access can be allowed or restricted to certain domains. Keep in mind that if you add blocked domains, all other domains will be allowed but if you add allowed domains, all other domains will be blocked. In the above screenshot, all domains are allowed except the badguys.com. Allowing or blocking domains in this section is not required. Because by default your organization can communicate with all external domains, you can ignore this setting.
Configuring Guest Access for Teams
To configure Guest access, go to Teams admin center -> Org-wide settings -> Guest access. If this setting is disabled, enable it.
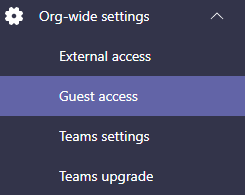
Configure the individual settings as necessary. For example, disable any settings you don’t want Guests to use, such as Allow Meet Now or Delete sent messages. These settings will depend on your organization’s security and privacy policies.
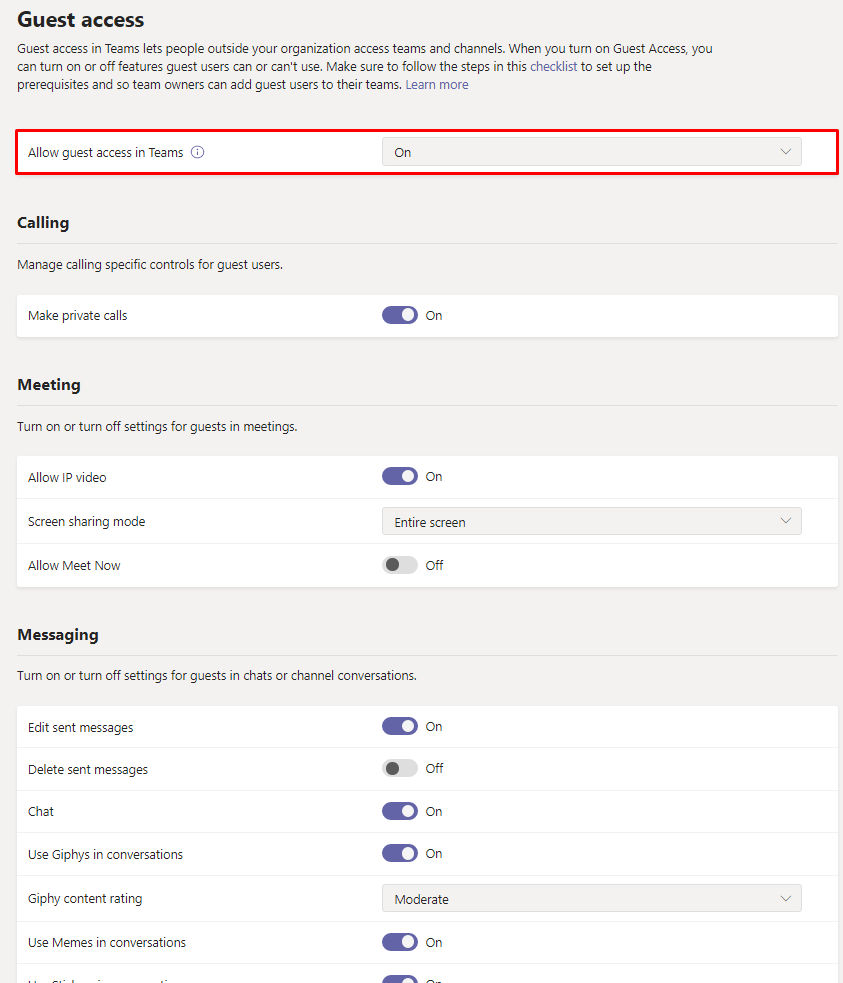
There are several settings under Teams admin center -> Org-wide settings -> Teams settings that should also be configured. However, they are out of scope for this article.
Next, open the Microsoft Teams desktop app. If you don’t have the app, download it from Microsoft. Although you can use the Teams app in your browser, this is the preferred method of using Teams.
Launch the Teams Desktop app and sign in to your Microsoft 365 user account.
Go to Teams -> More options (the three dots) -> Manage team.
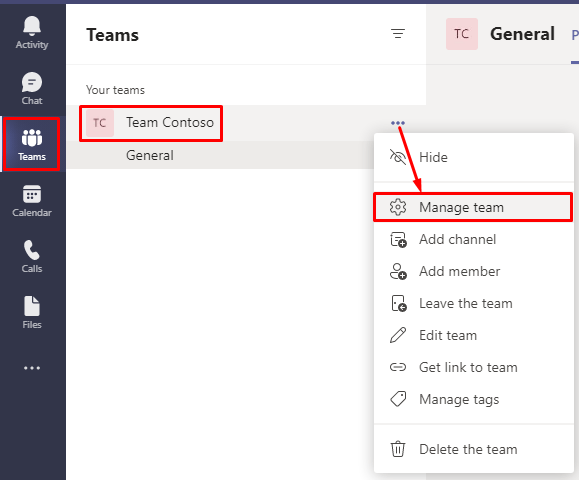
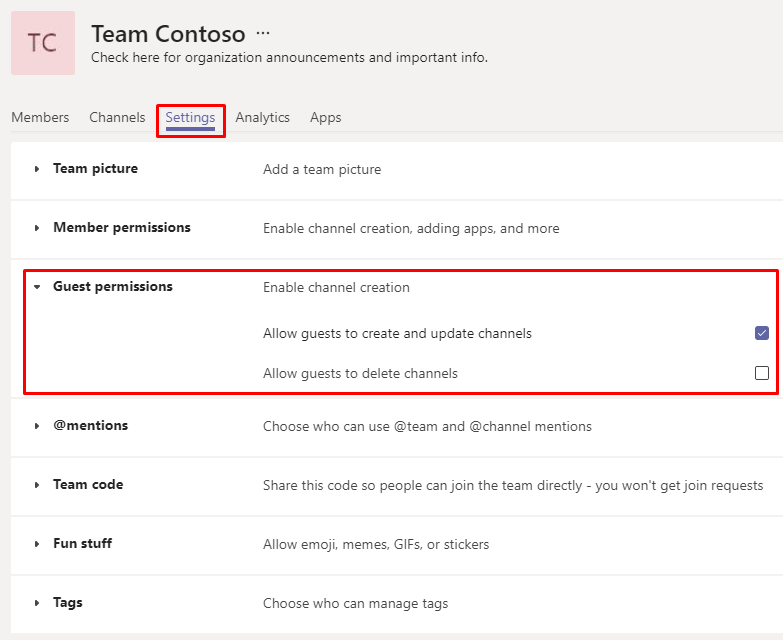
Select the Settings tab, expand the Guest permissions section, and select the options you want.
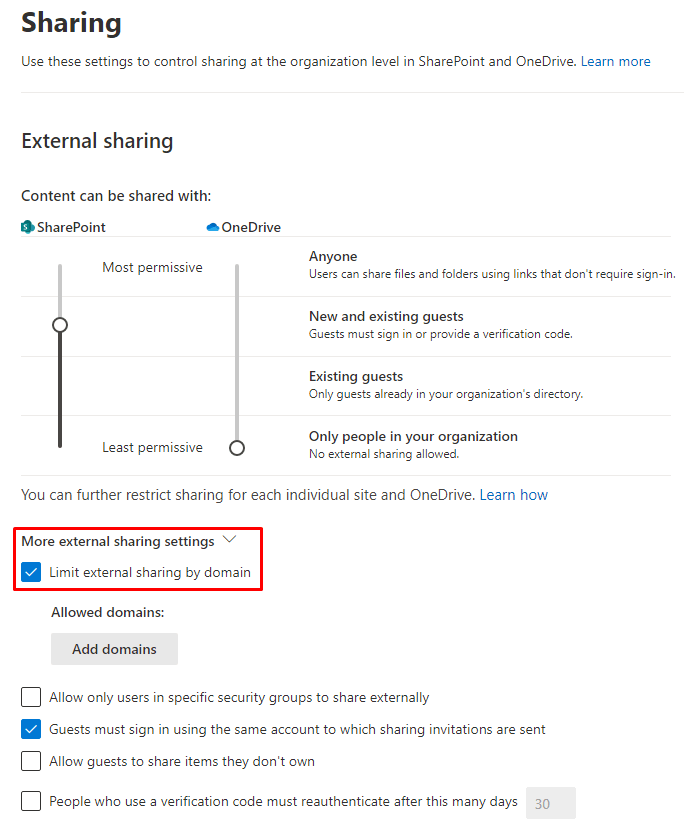
Configure SharePoint Settings for External Sharing
Go to SharePoint admin center -> Policies -> Sharing and configure the necessary settings for Guest access. For example, if for security reasons you are limiting external sharing by domains, select Add domains under Allowed domains, then add only the specific domains, such as Gmail.com or Outlook.com, so the external users in these domains can join as guests.
Enable Guest Settings for Microsoft 365 Groups
This is yet another setting required for guests to be able to become a member of Microsoft Teams. Keep in mind that SharePoint Online, Teams, and Microsoft 365 Groups are interconnected. In order for guest accounts to have access to Teams, you need to ensure that guest settings for Microsoft 365 Groups are enabled.
- Go to Microsoft 365 admin center.
- In the left pane select Settings. If you don’t see a link for Settings, type settings in the Search box at the top of the page and select Org settings.
| TIP: The Settings section in Microsoft 365 admin center contains several links, such as Domains, Search & intelligence, Org settings, Integrated apps, and Partner relationships. You will find it between Support and Setup. If you don’t see the Settings link, select Show all at the bottom of the left pane and you should see the Settings link. Of course, it’s much easier to use the search box at the top of the page to search for the items you’re looking for. |
On the Services tab, select Microsoft 365 Groups in the list of services.

If you want to allow group owners the ability to add external users as guests, select the first check box. If you only want Microsoft 365 admins to add guests then leave this box unchecked.
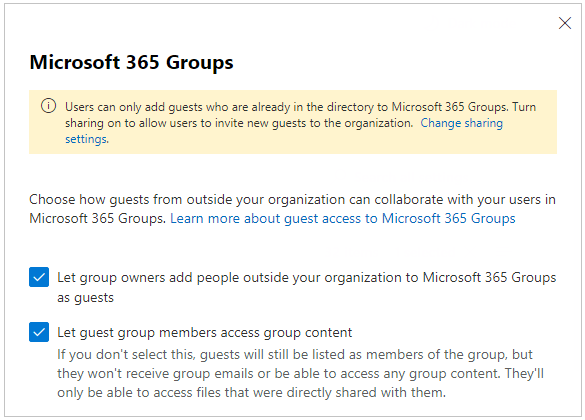
Click Save to apply your changes.
As the message in the screenshot indicates, you haven’t configured the sharing settings so the all users in your organization won’t be able to invite guests. They will only be able to add guests who were previously added by the Global Admin to Azure AD. If your organization is concerned about security, users should be only allowed to add guests that are already in the organization’s Azure AD.
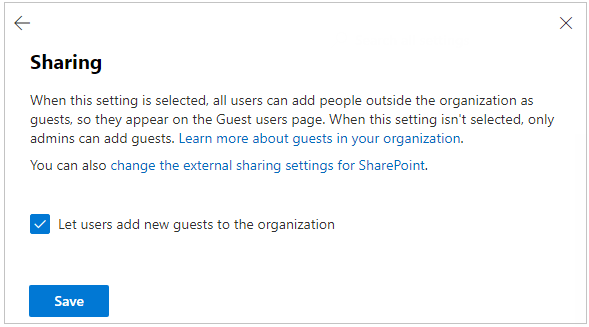
If you want every single person in your organization to have the ability to invite external users then click the link Change sharing settings in the above screenshot. Select the box Let users add new guests to the organization and click Save. Only use this option if your organization understands the security implications of this setting.
Adding Guests to the Teams Channel
Microsoft 365 admins can always add guests to the Teams. The owner of a team can also add a guest to the team. The guest will receive a welcome email from the team owner, with information on how to join the team. How the guests join the team depends on the type of account they have. They can use a Microsoft Account, or their work or school account in Azure AD (e.g. BillG@Contoso.com) to sign in. Guests that don’t have a Microsoft Account (e.g. user@gmail.com) are sent a one-time passcode authentication to join Teams. The process is fairly simple. Let’s say a Gmail user accepts the invitation to join a team, he/she sends a request for a temporary code, the code is emailed to the user, the user then enters the code and signs in to access Teams.
| Microsoft Accounts are used to sign in to Microsoft Office 365, Outlook.com, OneDrive, Skype, Windows Phone, Xbox Live, and other Microsoft services. |
Once the guest user joins Teams, the guest’s access to resources depends on the permissions set by the Teams owner or Global admin. The guest can pretty much work in Teams just like any other member of the team, access files, attend Teams meetings, chat, etc.
To add a guest member, go to the Teams where you want to add the member. Select the More options (three dots) and then select Add member.
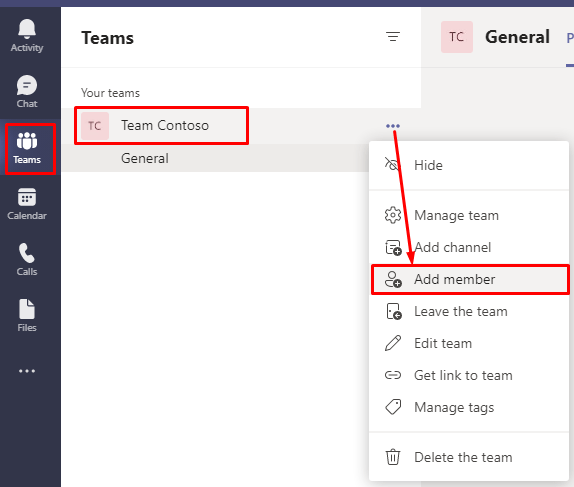
Depending on your configuration settings, the external user may have to exist in the Azure AD before you can add him/her to the Teams. Once the external guest has joined the Teams, other members of the team will be able to collaborate with the user just like they do with the other users within the organization. However, the user will have to abide by any restrictions that may have been imposed on external users.
Helpful Links
Here are some useful links related to the topics covered in this article.
- Adding guests to Microsoft 365 Groups
- Comparison of Team Member and Guest Capabilities
- Guest Access in Microsoft Teams
- Manage external access in Microsoft Teams
| Thanks for reading my article. If you are interested in IT consulting & training services, please reach out to me. Visit ZubairAlexander.com for information on my professional background. |
Copyright © 2021 SeattlePro Enterprises, LLC. All rights reserved.



