Understanding TCP/IP Port Numbers

My students often ask me about the common TCP/IP port numbers that they need to know for Microsoft certification exams. A lot depends on the exam you are taking. For example, for Active Directory exam it will be helpful to know the ports that Active Directory uses, for SQL Server the ports used by SQL Server service, and so on. Here are some basic things to know about TCP/IP port numbers.
According to Techopedia, “A port number is the logical address of each application or process that uses a network or the Internet to communicate.” The port numbers range from 0 to 65,535. These virtual ports are used for different purposes. The following table summarizes the designation and purpose of the three main categories of port numbers.
| Port Number | Designation | Purpose |
| 0 – 1023 | Well-known or common ports | These are reserved and assigned ports for common TCP/IP applications. |
| 1024 – 49151 | Registered ports | These ports are used by vendors for various applications and are not assigned. However, vendors can register their port number with ICANN. |
| 49152 – 65535 | Dynamic or private ports *** | These ports are not reserved or registered. They are used temporarily so they’re assigned dynamically. Dynamic ports are only used by clients and are ephemeral (short-lived). |
*** Windows Server 2008 and later servers and Windows Vista and later clients use the dynamic port range 49152 – 65535. Older Windows versions before Window Server 2008 and Windows Vista used the dynamic port range 1025 – 5000. If you either use a mixture of older and newer versions of Windows or only use older versions of Windows on your network, you must enable connectivity over the 1025 – 5000 range as explained in this Microsoft article.
Common TCP/IP Port Numbers
Here are some of the common TCP/IP port numbers that are good to know for certification exams. Obviously, you can always add more port numbers to this list. However, if you are new to port numbers, this is a good start. There is no easy way to memorize the port numbers. Over time you will get more comfortable with them. Network and security professionals who install, configure, and manage servers, routers, and firewalls for a living get to know the port numbers really well.
Here’s a list of 20 well-known port numbers and the associated service. For a more detailed list, download the PDF document TCP/IP Port Numbers.
TCP 20 FTP (File Transfer Protocol – Data)
TCP 21 FTP (File Transfer Protocol – Control)
TCP 22 SSH (Secure Shell – Remote login protocol)
TCP 23 Telnet
TCP 25 SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
TCP 53 DNS (Domain Name System)
TCP 67 BOOTPS (Bootstrap Protocol Server)
TCP 68 BOOTPC (Bootstrap Protocol Client)
TCP 80 HTTP (HyperText Transport Protocol)
TCP 88 Kerberos
TCO 110 POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3)
TCP 119 NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol)
TCP 123 NTP (Network Time Protocol)
TCP 137 NetBIOS (NETBIOS Name Service)
TCP 138 NetBIOS (NETBIOS Datagram Service)
TCP 139 NetBIOS (NETBIOS Session Service)
TCP 143 IMAP (Internet Mail Access Protocol)
TCP 161 SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
TCP 389 LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)
TCP 443 HTTPS (HTTP secure – used for SSL)
In Windows operating systems, the services file lists the well-known, registered, and dynamic ports that are used by the applications. The file is located in the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc folder. The services file doesn’t have an extension, but you can open it with a Notepad. Because this is a system file, users should not be making any changes to it. There are a couple of files in this folder (hosts & lmhosts) that I have to update once in a while, especially when I am troubleshooting name resolution issues. However, that discussion is out-of-scope for this article.
How Do You Decide Which Port Number to Use?
Let’s say you want to assign a port to your application. Obviously, you don’t want to choose a port that’s already reserved for an application, e.g., DNS, otherwise a port conflict could cause service disruption and all kinds of problems. So, how do you decide which port number to use? You can pick a port number above 50,000 because they are not registered and unlikely to cause a conflict. Another way to ensure you won’t have a port conflict is to look at the list of the TCP/IP Port Numbers and pick a port that you know for sure your network doesn’t use. What I prefer to do is pick a port number that’s usually used by a malware. For example, TCP port 21544 is used by GirlFriend Trojan and TCP port 22222 is used by Prosiak Trojan. It’s highly unlikely that you have these trojans running on your network, so you might as well utilize these ports. Look at the end of the listing in this downloadable PDF and you will find a lot of ports used by trojans. Keep in mind, port numbers above 49152 are not reserved, they are assigned dynamically.
Using Custom Port Numbers
If you are interested in a career in cybersecurity or computer networking, you should really spend time on learning about TCP/IP port numbers. The more you learn about the ports, which are essentially an entry way to your network, the better off you will be. In an environment where security is really important, I encourage my clients to use custom port numbers for some of their services. For example, the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) in Windows computers listens on port 3389. Because cybercriminals are aware of this fact and are likely to attack port 3389, you can change the port number to an unused port number within your network, such as 1245 used by VooDoo Doll Trojan. Cybercriminals often use scripts that scan the default port numbers on computers. By changing the default port for RDP, you will make it difficult for hackers to guess your RDP port number. Yes, there are ways to find out about the open ports on your computers, but there are also ways to configure your systems in a way that no one would know whether you have any port open on your computer, or even if a port exists. This would be a good topic for a future article.
For step-by-step instructions on setting up a firewall rule in Windows 10 that will change your default RDP port, check out my article Secure Your Computer by Modifying the Default RDP Port Number. You can use this technique to secure RDP port not only on your network servers at work.
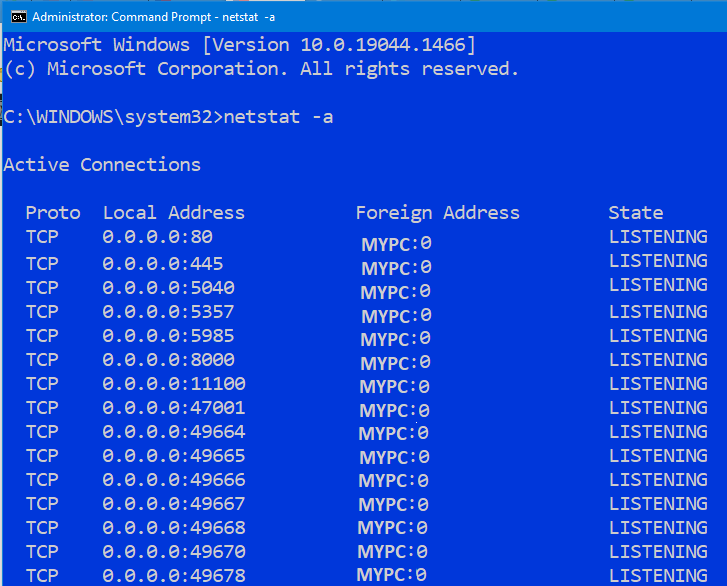
One final note. Before you change the default port number, make sure you understand the consequences. You only want to modify the default port number if you are 100% sure your computer is not using that port for another service. If you are working on a network, you want to make sure that no other device on your entire network is using that port number. If you run into a problem, simply change the port number back to its default value. You can use netstat -a at the command prompt to see which ports are open on your computer. The ports that are open will display LISTENING in the State column.
There is so much more to know about TCP/IP port numbers. Microsoft has an excellent article about network port requirements (see Additional Resources below), which also lists the port numbers used by various Windows services. It’s loaded with good information. I encourage you to read that article and save it for future reference.
Additional Resources:
- IANA-Assigned Service Name and Port Numbers Registry
- IANA IPv4 Address Space Registry
- Secure Your Computer by Modifying the Default RDP Port Number
- Service Overview and Network Port Requirements for Windows
| Thanks for reading my article. If you are interested in IT consulting & training services, please reach out to me. Visit ZubairAlexander.com for information on my professional background. |
Copyright © 2022 SeattlePro Enterprises, LLC. All rights reserved.